Error Tracker¶
Error Tracker is a python app plugins for Flask and Django, that provides many of the essentials features of system exceptions tracking.
Features¶
- Mask all the variables, including dict keys, HTTP request body which contain password and secret in their name.
- Recorded exceptions will be visible to the configured path
- Send notification on failures
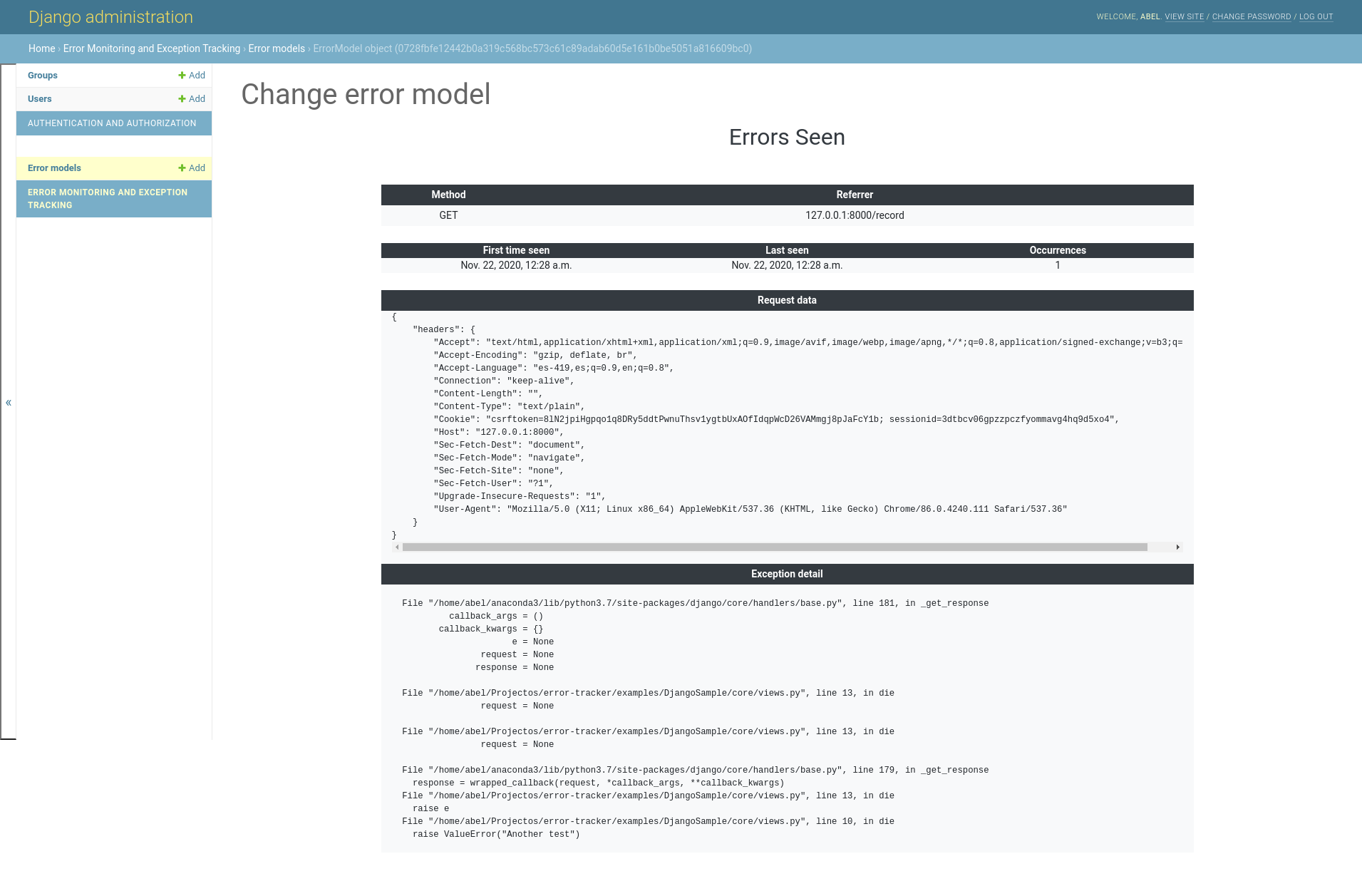
- Record exceptions with frame data, including local and global variables
- Raise bugs or update ticket in Bug tracking systems.
- Provide customization for notification, context building, ticketing systems and more
Exception Listing
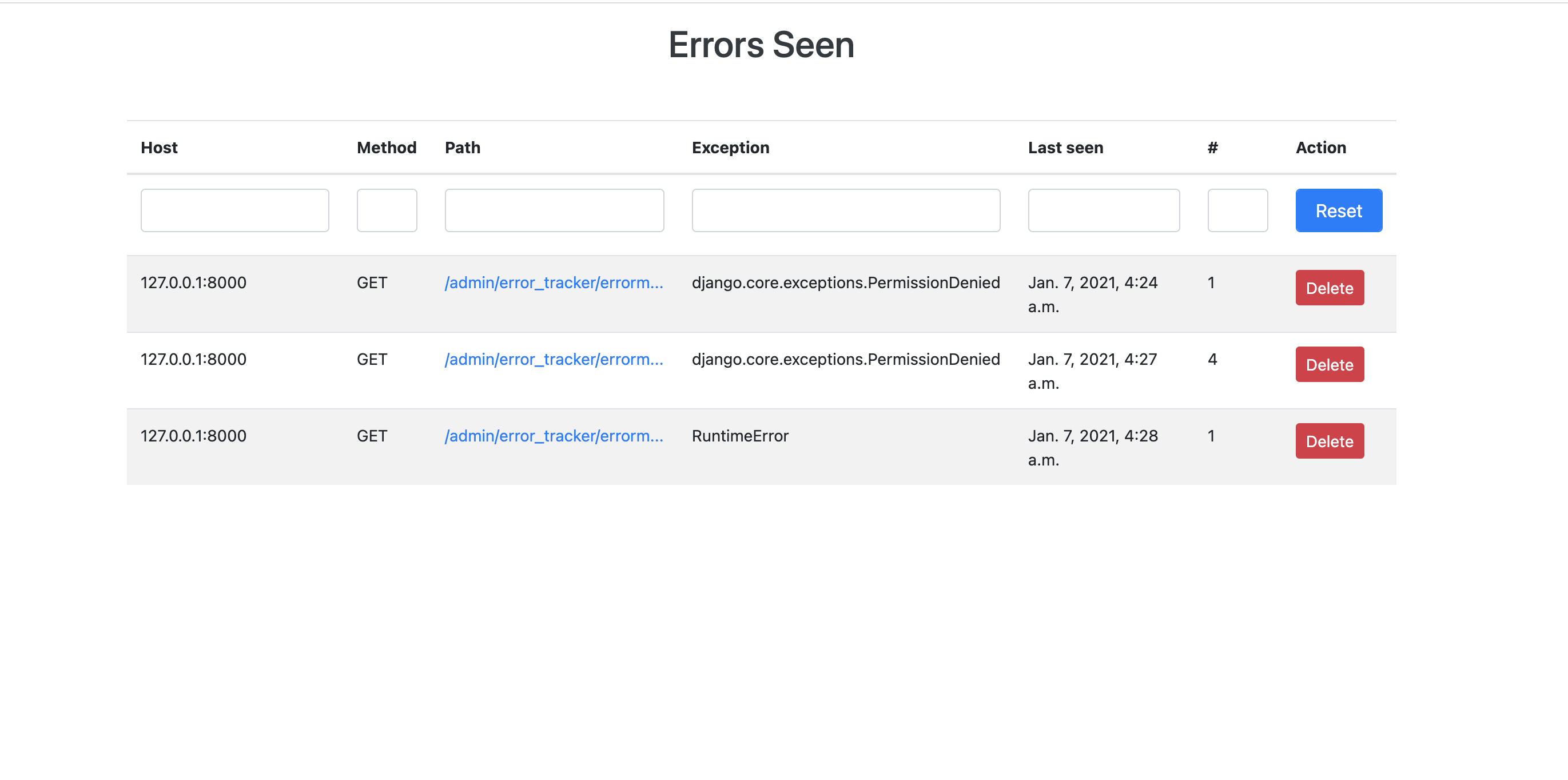
Detailed Exception

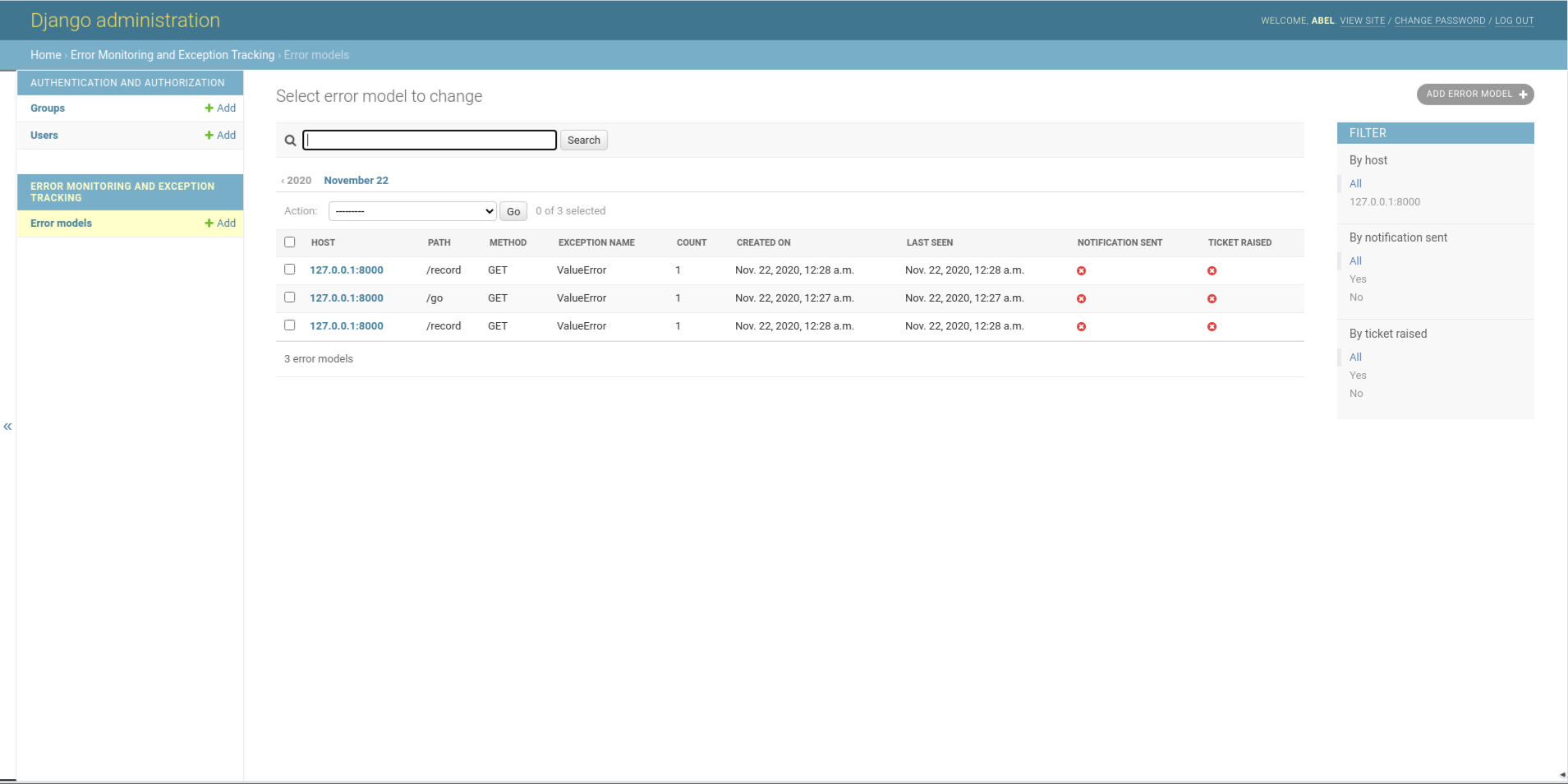
Admin dashboard
Quick start¶
Installation¶
To install Error Tracker, open an interactive shell and run:
pip install error-tracker
Error Tracker can be used with
- Standalone Python application
- Flask Application
- Django Application
Using Error Tracker as simple as plugging any other module.
Recording exception/error¶
An error/exception can be recorded using decorator or function call.
- To record the error using decorator, decorate a function with
track_exceptionorauto_track_exception - Where as to record error using function call use
capture_exceptionfunction. - Exception detail can be written to a file, console or logger etc call method
print_exception
All the data will be stored in the configured data store and these data will be available at configure URL path.
Flask App setup¶
An instance of AppErrorTracker needs to be created and have to be configured with the correct data.
Monitoring feature can be configured either using object based configuration or app-based configuration,
the only important thing here is we should have all the required key configs in the app.config otherwise it will fail.
Note
Exception listing page is disabled by default. You need to enable that using view_permission parameter. view_permission function/callable class must return True/False based on the current request detail. This method would be called as view_permission(request).
For object based configuration add settings.py
...
APP_ERROR_SEND_NOTIFICATION = True
APP_ERROR_RECIPIENT_EMAIL = ('example@example.com',)
APP_ERROR_SUBJECT_PREFIX = "Server Error"
APP_ERROR_EMAIL_SENDER = 'user@example.com'
app.py
from flask import Flask
from flask_mail import Mail
import settings
from error_tracker import AppErrorTracker, NotificationMixin
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
...
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config.from_object(settings)
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
class Notifier(Mail, NotificationMixin):
def notify(self, request, exception,
email_subject=None,
email_body=None,
from_email=None,
recipient_list=None):
message = Message(email_subject, recipient_list, email_body, sender=from_email)
self.send(message)
mailer = Notifier(app=app)
# enable for all users
class ViewPermission(ViewPermissionMixin):
def __call__(self, request):
return True
error_tracker = AppErrorTracker(app=app, db=db, notifier=mailer, view_permission=ViewPermission())
....
....
# Record exception when 404 error code is raised
@app.errorhandler(403)
def error_403(e):
error_tracker.capture_exception()
# any custom logic
# Record error using decorator
@app.errorhandler(500)
@error_tracker.track_exception
def error_500(e):
# some custom logic
....
Here, app, db and notifier parameters are optional. Alternatively, you could use the init_app() method.
If you start this application and navigate to http://localhost:5000/dev/error, you should see an empty page.
Django App Setup¶
We need to update settings.py file as
- Add app
error_tracker.DjangoErrorTrackerto installed apps list - Add Middleware
error_tracker.django.middleware.ExceptionTrackerMiddleWarefor exception tracking [1]. - Other configs related to notification
- Add URLs to the list of URL patterns
- Enable django admin site (optional).
| [1] | This should be added at the end so that it can process exception 1st in the middleware call stack. |
Note
Exception listing page is only enable for super users by default. You can enable for others by providing a custom implementation of ViewPermissionMixin. This class must return True/False based on the current request, False means not authorized, True means authorized.
...
APP_ERROR_RECIPIENT_EMAIL = ('example@example.com',)
APP_ERROR_SUBJECT_PREFIX = "Server Error"
APP_ERROR_EMAIL_SENDER = 'user@example.com'
# optional setting otherwise it's enabled for super users only
APP_ERROR_VIEW_PERMISSION = 'permission.ErrorViewPermission'
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'error_tracker.DjangoErrorTracker'
]
MIDDLEWARE = [
...
'error_tracker.django.middleware.ExceptionTrackerMiddleWare'
]
We need to add URLs to the urls.py so that we can browse the default pages provided by Error Tracker
from error_tracker.django import urls
urlpatterns = [
...
url("dev/", include(urls)),
]
To enable the error tracker in the admin site add this line in your settings.
APP_ERROR_USE_DJANGO_ADMIN_SITE = True
Using With Python App (NO WEB SERVER)¶
Choose either of the preferred framework, flask or Django and configure the app as per their specifications. For example, if we want to use Flask then do
- Flask App
- Create Flask App instance
- Create Error Tracker app instance
- DO NOT call run method of Flask app instance
- To track exception call
capture_exceptionmethod
- Django App
- Create Django App with settings and all configuration
- Set environment variable DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE
- call
django.setup() from error_tracker import error_tracker- To track exception do
capture_exception(None, exception)